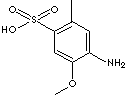
| p-CRESIDINE-o-SULFONIC ACID | |||||||||||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
|||||||||||
| CAS NO. | 6471-78-9 |
|
|||||||||
| EINECS NO. | 229-319-5 | ||||||||||
| FORMULA | C8H11O4NS | ||||||||||
| MOL WT. | 217.24 | ||||||||||
| H.S. CODE | |||||||||||
|
TOXICITY |
|||||||||||
| SYNONYMS | 4-Amino-5-methoxy-2-methylbenzenesulfonic acid; | ||||||||||
| 5-Methoxy-2-methylsulphanilic acid; 4-Amino-5-methoxy-o-toluenesulfonic acid; | |||||||||||
|
SMILES |
O=S(=O)(O)c1c(cc(N)c(OC)c1)C |
||||||||||
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
||||||||||
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
|||||||||||
| PHYSICAL STATE | white to gray powder | ||||||||||
| MELTING POINT |
|
||||||||||
| BOILING POINT | |||||||||||
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | |||||||||||
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
Soluble (6208 mg/l) |
||||||||||
| AUTOIGNITION |
|
||||||||||
| VISCOSITY | |||||||||||
| PH |
|
||||||||||
| VAPOR DENSITY | |||||||||||
| NFPA RATINGS | Health: 2; Flammability: 1; Reactivity: 0 | ||||||||||
| FLASH POINT | |||||||||||
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions | ||||||||||
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS |
|||||||||||
Cresidine is
the trivial name for methyl anisidine or methoxy toluidine.
There are three isomers, ortho-,
meta-T, and para-cresidine. The
prefix indicate amino group positions relative to the
methoxy group on the same benzene ring. Aromatic
amines Cresidine, anisidine, toluidine are all homologous to aniline,
the simplest aromatic amine. Aromatic
amines are the fundamental
materials in the dye manufacturing industry. They are
also important in the manufacture of
rubber-processing chemicals, explosives, plastics, antioxidants, drugs, pesticides and other
chemical compounds.
Aromatic
amines take part in many kinds of chemical reactions and offer many industrial
applications.
p-Cresidine-o-sulfonic acid is a base material to produce cresidine food dyes. Wikipedia Linking: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cresidinesulfonic_acid |
|||||||||||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | |||||||||||
|
APPEARANCE |
white to gray powder | ||||||||||
| ASSAY |
96.0% min (Dry basis), 80.0% min (wet basis) |
||||||||||
| FREE CRESIDINE |
0.2% max |
||||||||||
| TRANSPORTATION | |||||||||||
| PACKING | |||||||||||
| HAZARD CLASS | |||||||||||
| UN NO. | |||||||||||
| SAFETY INFORMATION | |||||||||||
|
Hazard Symbols: T, Risk Phrases: 45-22, Safety Phrases: 53-45 |
|||||||||||